Still don’t know what an Internet search algorithm is or don’t understand how some of them work? If you have an online business or a website, you will intuit that, knowing the basic operation of search engines like Google, will help you create content adapted to what they consider “deserving” of ranking first.
It is that, if until now you have been writing on your blog or that of your business content without taking into account minimally how a search algorithm works, it is possible that you are hitting blind.
In addition, surely among all the information that you have read and heard to date about penguins, pandas and so many other animals, perhaps you still do not clarify the differences between them. And to get off to a good start, there’s nothing better than taking a look at the general definition of what an algorithm is.
What Is An Algorithm?
An algorithm is an ordered and systematic set of rules and logical operations that allows us to perform a calculation to find the solution to a specific type of problem.
Now, if we take this term to relate it to the searches in the network, we could define it:
What Are Internet Search Algorithms?
An Internet search algorithm is a set of instructions that describe the procedure to be followed in order to find a specific and concrete result in the network, within a larger data structure.
Perhaps explained in this way sounds complicated, but if we approach the term from the computer point of view, we find a clearer explanation, since an algorithm is a fundamental concept in this field.
This word supposes a precise prescription of the actions that must be carried out to reach a specific end.
Thus, we can assume that any instruction is an algorithm if:
- Its points do not allow different variants of development.
- Indications are provided for all possible scenarios.

But What Are We Talking About When We Ask Ourselves What Is An Internet Search Algorithm?
When we go looking for something (for example, in Google ), what we want is an exact and filtered answer , not millions of pages that have nothing to do with our request.
An algorithm is then the perfect tool to limit that search to the minimum expression, since it is a computer program that looks for clues to give you exactly what you have asked for.
At the same time, these are also formulas that identify your questions and turn them into a list of potential answers. To do this, Google’s search algorithms rely on hundreds of unique cues or factors .
These factors make it possible to almost guess what you are really looking for on the Internet to offer you a list of possible answers, ordered from highest to lowest according to their relevance to that particular search.
So can I find out how a search algorithm like Google works?
Although, for obvious reasons, we cannot completely decipher it, we can know some basic aspects and, thanks to them, deduce the minimum requirements that this algorithm has been taking into account.
And of course we can get information about how it works to optimize our SEO strategy . However, it is not always easy to obtain such information.
That is why, I will tell you about the particularities of Internet search algorithms and the histories of three of the main search engines today.
How Do The 3 Most Popular Search Algorithms On The Internet Work?

I want to share with you today a topic that more and more people are interested in on the internet: how a search algorithm works and which one is treading stronger today.
As we well know, talking about the Internet is almost talking about our friend Google, who periodically updates his search algorithm, improving it even more and making him smarter.
A couple of its objectives for a while now, for example, are to prioritize the WPO of a website and navigation from mobile devices, increasingly used in our society.
But not only Google has been interested in this aspect, but all major search engines, in its intention of continuous improvement.
In short, we have before us a platform that, with its search algorithm, increasingly rewards quality content and, above all, offers users the content that best suits their search intention or «query».
Bing, Yahoo! o Yandex are also in the process of improving their search algorithms so that users achieve the best results by “investing” the shortest time possible in conducting an Internet search.
Of course, these changes affect SEO positioning strategies of marketers and web domain owners.
Talking about the most important means, of course, including the most popular search engines:
- Bing
- Yandex
Of course, it is these three that we will deal with in this post.
Shall we start?
What Are The Best Known Search Engines And What Are Their Search Algorithms Like?

Next, we will see which are the most popular search engines in the world and review the evolution of their formulas and updates.
► Yandex
This program was created in 1988 by the company CompTek, although the Yandex-Web search engine was presented to the world on September 23, 1997.
The first version of the search program called “Yandex” appeared in 1993, although at that time it was rather a tool for finding information within a single website.

Today “Yandex” is the largest Internet company in Europe , with a capitalization of $ 10 billion (according to 2013 data).
For its part, the search engine «Yandeks.Poisk» in early 2013 was the fourth in the world, with 4.84 billion search requests, and the second among non-English speaking engines after “Baidu” .
Yandex search algorithm and updates
In 2008 Yandex released an update called Magadán (by the way, Yandex names its updates taking the name of different Russian cities).
This update solved the problem of interpreting abbreviations and transliteration and, in addition, the correlation between words with the same root.
That update is updated again a few months later by adding additional ranking factors (such as prioritizing exclusive content ).
In 2008 and 2009 Nakhodka and Arzamás saw the light, whose objective is to improve the results for «queries» with conjunctions and prepositions.
Thus, SERPs offer more informative results compared to the previous proportion of previous results; Also from here they focus on aspects related to geolocation when searching.
At the end of 2009, Yandex announces the Snezhinsk update : a more complex technology that analyzes the content of the page taking into account a greater number of factors.
Hence, relevant and quality content became an essential factor.
September 2010 arrives and Obninsk appears, focusing on SEO-links ( paid backlinks ) and reducing their impact on page positioning.
In August 2010 the search begins to be personalized, but it is in December 2012 when Kaliningrad was born, which provides a global search customization according to the user’s interests.
Thanks to Kaliningrad, information about that user’s actions will be updated once a day, and will be segmented taking into account the duration of the search and the customization of the search.
So the impact of SEO came not only from backlinks and searching for important keywords , but from everything together: the design, the usability, the content, etc.
After Kaliningrad’s modification called Dublin (which was released in 2013), the search engine begins to memorize the user’s most recent actions.
Recently, in April 2015, paid backlinks are no longer an influencing factor when ranking web pages.
When paid link domains start to lose position, Yandex aims to get rid of backlink spam and for domain owners to focus their SEO efforts on improving content , usability, design and service.
This means (to close the topic of Yandex updates) that from that moment, it is no longer significant to get those backlinks that were so important within SEO strategies on RUnet.
► Bing
Bing is the quintessential Microsoft web browser, introduced in May 2009.
In July 2009, Microsoft and Yahoo! Announce Bing to Replace Yahoo! Search , at which time they also launch the new web spider, called MSN bot 2 (previously called MSN Search).
All this shows that this is a relatively new search engine. Despite this, Bing ranks second in the ranking of the most popular search engines according to traffic volume.

Despite this popularity, the changes to its search algorithm are not as famous as those of Google or Yandex and, unlike those two, Bing does not reveal the updates made and does not give them names as Yandex and Google do.
That is why we are left with nothing more than to describe the differences in search results and positioning.
For years Bing has been paying special attention to:
- The images.
- The flash.
- The videos.
- The audios.
Today, this search engine pays more attention to direct keywords . Therefore, if you want to adapt your website for a better positioning in Bing, you are obliged to build your SEO strategy on certain and specific keywords.
In October 2011, Microsoft announced that it was working on an update that received the name of “Tiger” (in this case, it did name it), which aimed to provide more relevant and faster results for the user, after improving processing What are you laughing at.
Backlinks, unlike social media activity, are not in Bing’s favor. In fact, it has always shown a much greater predilection for engagement on social platforms.
The time has come to talk about the world’s largest and best-known search engine.
In a conference closed in early May 2014, the Google representative mentioned that 60 billion documents are indexed today . Imagine the current amount, already at the end of 2018 …

As you can see from the test results, the Google search counter is limited to 25,270,000,000, which number is also affected by the filters built into the dispensing algorithm.
The Google search engine was created as a school project by Stanford University students Larry Page and Sergey Brin.
In 1996 they work for the search engine system called BackRub and, based on it, they create a new search engine two years later: Google.
From the beginning they begin to apply a transparent OKR control method that later defines the company’s corporate line in terms of planning and development.
What Are The Different Search Algorithms That Google Has Had Throughout ıts History?
Below, I will show you the different variations of the Google algorithm, all in chronological order and according to the meaning and function of each update:
1. Google Panda (“Caffeine” Update)
An update called Caffeine is announced on August 10, 2009, promising faster crawling, expansion and integration of indexing and near real-time ranking.
The launch takes place, finally, in June 2010.
In February 2011, Google launched Panda , a broad-spectrum update that affects 12% of search queries .
This update seeks to take active action against spam, content farms, web scraping, and high ad percentage websites compared to content percentage.
During 2011, Google updates Panda and goes to Panda version 2.1.
The Internet giant makes permanent changes, with the aim of significantly improving both indexing and user experience and its considerable improvement.
After launching Panda 2.4, the search algorithm also begins to work in all languages except Chinese, Japanese, and Korean.
In May 2014 Panda 4.0 is released, to end the year with the update to version 4.1.
And in 2015, Google integrates Panda to its general search core .
»Google Panda penalty example
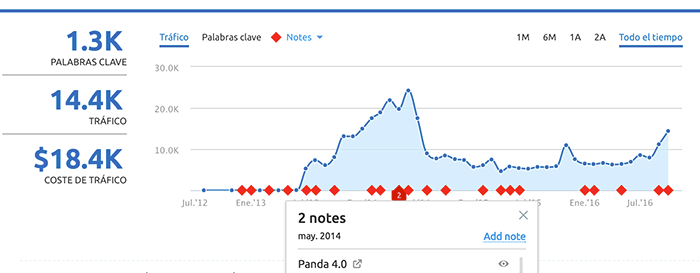
2. Algorithm «Freshness»
Freshness is released in November 2011, an update that prioritizes the latest search results .
But it is not until February 2012, after the launch of Venice, that search results are prioritized in relation to geolocation.
3. Google Penguin (Goodbye to ‘Black Hat’)
In April of the same year, Google Penguin update was released.
This update was born with the idea of penalizing websites that use ‘black hat SEO’ techniques to artificially improve the positioning of a domain.
Google Penguin considers as a priority to end spamdexing , that is, one of the methods to manipulate the relevance of pages indexed by a search engine.
At the same time, the main objective is to show the highest quality websites at the top of Google’s search results.
In September 2016, Penguin is integrated into the main search algorithm. Now it works in real time and is much more granular.
It no longer affects the ranking of an entire website, but rather each URL individually.
»Google Penguin penalty example
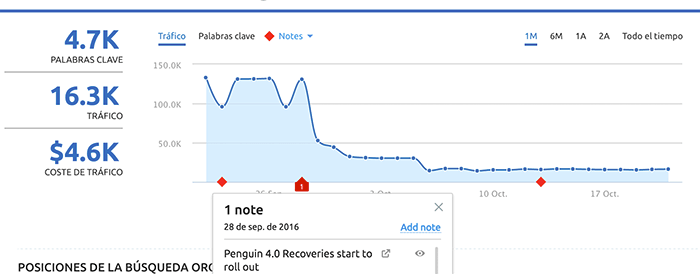
4. Google Hummingbird
Between August and September 2013 Google Hummingbird appears, considered the first major update after Caffeine, and aimed primarily at improving the indexing process .
In contrast to other search algorithms more focused on each query word separately, Google Hummingbird (in addition to taking each word into account) prioritizes the general query based on the phrase or sentence.
Google Hummingbird’s goal is for the search engine to understand the relationships between various keywords and multiple concepts.
With all this, Google aims to make the search more humane, and for this it bets on semantic searches in order to obtain more relevant results for the user.
Thus, Google Hummingbird ensures a better positioning of long-tail keywords , which become more natural to answer real user questions.
How does this search algorithm affect content creators?
This, logically, makes it more malleable by aligning it with the natural use of the language, adapted to real conversations and not to pure and hard keywords that SEO specialists attribute to their web pages.
Another major update, Google Pigeon, was launched in 2014, with the aim of prioritizing close search results, something very beneficial for local businesses and entrepreneurs (and, of course, for the user).
In addition, for security reasons, in that same year Google announced its preference for websites that use the HTTPS protocol.
In 2015, the search engine search engine released a new update that gives priority to the websites that show up best on mobile, responsive devices, not affecting search results from the computer (for the moment …). In turn, Google insists that the websites are ‘mobile friendly’.
To that end, in early March of that year, it warned webmasters of its intention to launch an update that allows users to receive even more relevant and friendly results for their mobile devices.
Below I share with you an infographic that summarizes the entire guide, which could continue until the coming years, in which Google’s search algorithms and the main engines existing on the network will surely be updated.

Source: josefacchin.com/







